
Protecting the Vulnerable Through Vaccination

Protecting the Vulnerable Through Vaccination

Protecting the Vulnerable Through Vaccination
Product Pipeline
Najít Technologies uses the proprietary HydroVax platform as our key technology for creating safer, more effective vaccines. In addition, we have developed a cGMP-compliant Vero cell line and have optimized virus growth conditions and purification strategies for manufacturing several vaccine candidates. A major advantage of our vaccine platform technology is the ability to rapidly incorporate new vaccine targets to our growing product pipeline and combine viral antigens to generate vaccines against entire virus families.
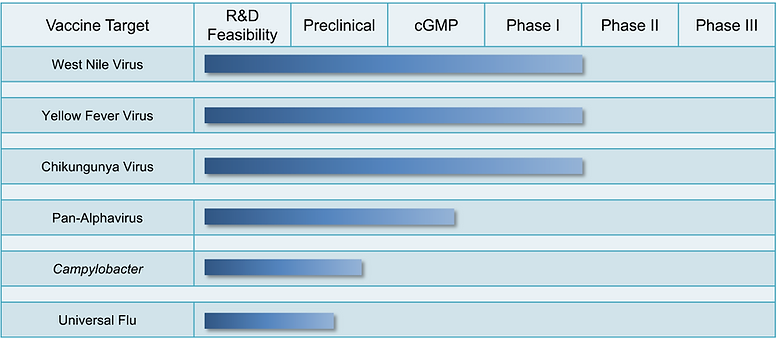
Yellow fever virus:
Similar to West Nile virus, yellow fever virus (YFV) is another member of the Flaviviridae family transmitted by infected mosquitos. YFV was at one time endemic in the United States and is still present in low- and middle-income countries, where infection can lead to mortality rates of 20-50%. The current live attenuated YFV vaccine was developed in 1936 and has not been modified or otherwise improved in over 50 years. According to the CDC, this vaccine causes 47 severe adverse events (defined as resulting in hospitalization, long-term disability, or death) per million vaccinations. More recent reports indicate that vaccine-associated neurological disease occurs at an approximate rate of 1 case per 10,000 vaccinations. YFV vaccination of infants <9 months of age has been contraindicated since the 1960’s due to high rates of vaccine-associated encephalitis in this age group. The overall mortality rate following YFV vaccination is estimated at 1 to 2 deaths per million doses. Further, YFV vaccination has been found to cause severe viscerotropic disease in a substantial number of patients >60 years of age (an incidence rate of approximately 1:50,000 doses administered) and these cases result in approximately 50% mortality. This indicates that YFV vaccination is not only contraindicated in infants but is also not recommended in the elderly due to the increased risk of severe and life-threatening disease. Increased monitoring efforts have also documented several cases of vaccine-related fatalities in young, otherwise healthy adults with no known pre-existing immune deficiencies.
Approximately 250,000 US civilian travelers and 750,000 US military personnel are vaccinated annually for travel to YFV endemic countries. However, at this time there is no licensed alternative to live YFV vaccination, putting a substantial number of people at risk for adverse reactions. To help fill this unmet need, NTI, in partnership with Oregon Health & Science University, has secured funding from the National Institutes of Health for development of a safer, inactivated YFV vaccine. This vaccine is based on NTI’s proprietary HydroVax platform, which can deliver inactivated vaccine formulations appropriate for use in immunologically vulnerable individuals, in addition to other healthy populations. Through this project, NTI plans to advance a second-generation YFV vaccine that can be used safely across all potential vaccine recipients while still eliciting robust antiviral immunity.
West Nile Virus:
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen belonging to the Flaviviridae family. WNV is transmitted primarily by infected mosquitoes, but other mechanisms of infection have been identified, including transmission through blood transfusion, organ transplantation, transplacental transfer, and through breast milk from an infected mother to her infant. Since its introduction into North America in 1999, WNV has spread across the continent. Recent studies suggest that at least 30 undiagnosed cases of WNV occur for every case reported and the true burden of WNV is likely closer to 3 million infections, resulting in an estimated 780,000 illnesses. While many instances of WNV infection are asymptomatic, reported mortality rates among WNV cases have ranged from 7–14%, with death rates among elderly patients ≥65 years of age reaching as high as 35%.
Although veterinary vaccines have been licensed, to date a human vaccine remains unavailable. With funding awarded through the National Institutes of Health (NIH), NTI partnered with Oregon Health & Science University and Washington University-St. Louis to develop an inactivated whole-virus WNV vaccine using its proprietary HydroVax platform, with pre-clinical studies demonstrating significant immunity and protection. NTI has now developed a second-generation WNV vaccine that has shown further enhanced immune responses that are up to 130-fold higher than previously observed with the original HydroVax technology (Quintel et al., Vaccine, 2019), and the company has recently completed cGMP manufacturing and initiated a Phase 1 clinical trial. This vaccine has the potential to be used by a broad and immunologically diverse population without the risk of rare, lethal infection associated with certain live viral vaccines.
Chikungunya virus:
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an emerging/re-emerging mosquito-transmitted pathogen responsible for explosive epidemics of febrile illness reported in at least 99 countries and characterized by debilitating polyarthralgia (severe joint pain). Between 2006 and 2007, ~1.4 million cases of CHIKV were reported in India, in addition to recent autochthonous outbreaks in Europe, as well as >1.7 million cases of CHIKV in the Caribbean and the Americas. While previous CHIKV outbreaks were not considered life threatening, the 2006 outbreak on the French island of La Reunion had an estimated case fatality rate of approximately 1:1,000. Although this disease is considered an important threat to those living in endemic areas, the US military, and international travelers, there is currently no licensed vaccine for the prevention of CHIKV illness.Using advanced manufacturing approaches, in conjunction with the novel HydroVax inactivation platform, NTI has developed a highly potent CHIKV vaccine candidate that fully protects against disease in established animal models. NTI has completed cGMP manufacturing of this vaccine candidate and initiated Phase 1 clinical testing.
Campylobacter:
Campylobacter species cause an estimated 400-500 million cases of bacterial gastroenteritis per year and represent one of the most important classes of human pathogens contributing to diarrheal disease throughout the world. The economic impact of Campylobacter-associated disease can be substantial, with annual costs in the US alone estimated at up to $5.6 billion. Additional studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between Campylobacter burden and childhood growth stunting, indicating that Campylobacter may be a key factor driving poor childhood growth and development outcomes in low resource settings. In total, these factors underscore why this pathogen is recognized as one of the most important global threats in need of targeted vaccine development. Despite the clear medical need, there is currently no Campylobacter vaccine available for use in humans. Using our HydroVax-based approach, we have developed a novel inactivated Campylobacter vaccine, demonstrating 83% vaccine efficacy in a natural exposure model among outdoor-housed non-human primates (Quintel et al., Science Adv 2020). These exciting results provide an important proof-of-concept to support the continued development of this vaccine candidate for prevention of Campylobacter-associated enteric disease in humans.
Universal Flu:
Despite over 70 years of vaccine development, influenza remains a persistent global challenge for public health authorities. The 2017-18 season was particularly severe with approximately 900,000 influenza-associated hospitalizations and 80,000 influenza-associated deaths in the US. On a global scale, the WHO estimates that seasonal influenza is responsible for 3-5 million cases of severe disease and up to 500,000 deaths each year. Although many potential approaches to developing a universal flu vaccine have been explored, to-date none have achieved major clinical success. NTI’s next-generation HydroVax technology represents a radical new approach to vaccine development in which site-directed oxidation-based inactivation of intact virus particles is used to prepare heat-stable vaccine formulations that are structurally similar to native live virus and induce long-lived protective immune responses. Our hypothesis is that the use of structurally intact HA and NA vaccine antigens in their native conformations on the surface of HydroVax-inactivated virus particles will provide broad and durable antiviral immunity.
Page stretcher (hidden element)
©2025 Najít Technologies, Inc. All Rights Resereved